Monopolistic competition
Monopolistic competition
A market is monopolistically competitive if there are many firms producing differentiated products and there are no barriers to entry or exit.
Assumptions of monopolistic competition
- There are many sellers and buyers
- The product is differentiated
- There are no or very low barriers to entry and exit
- Firms have some influence on the market price
- Each firm will seek to maximize profit
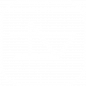
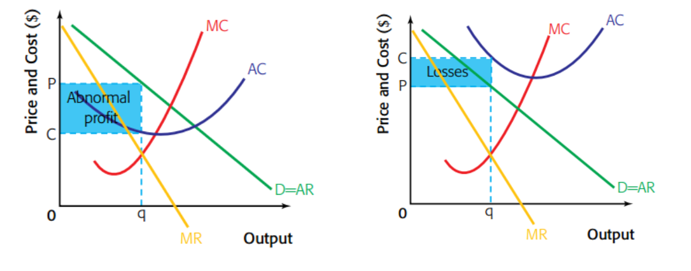
In short-run
- Product differentiation leads to a small degree of monopoly power, therefore to a negatively (downward) sloping D curve for the product.
- A firm can make abnormal profits / loss
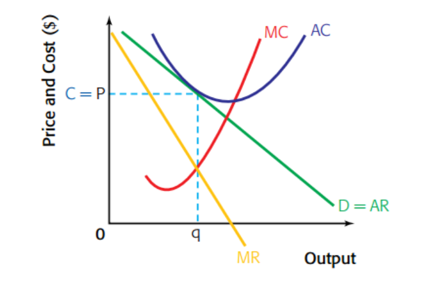
In the long run
- The abnormal profit will be competed away by the entry of new firms which will shift the original firm’s demand curve to the left. The process will continue until all firms in the industry are making normal profit.
- It operates above the minimum point of its average total cost curve giving a situation of excess capacity. So, there is **no productive efficiency. **
- P is not the price corresponding to where MC = AR, so there is also no allocative efficiency
Price competition
Firms compete on price when they lower their price in hopes of increasing the demand at the expense of another firm.
Non-price competition
When firms compete not on price, but engage in differentiation and advertising to encourage the purchase of their products.
- Advertisement
- Brand name creation
- Continuous product differentiation (packaging, design, special features, appearance)
- Personal selling
- Gifts & coupons
- Sponsorship of public events
- Quality of service
In SR/LR, a MC firm produces at output where there is neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency.
MC compares with PC
Advantages
- Consumers benefit from greater choice & variety of products due to product differentiation.
- Non-price competition leads to product development
Disadvantages
- Higher price and lower output than under PC due to consumer’s desire for product differentiation
- Lack of allocative & productive efficiency
Monopoly compares with MC
Advantages
- Ability to finance R&D from economic profit
- Need to innovate to maintain economic profit
- Possibility of economic of scale; possible to achieve dynamic efficiency
Disadvantages
- Higher price & lower output
- Lack of competition; lower incentive to improve and innovate
No Comments