Exchange rate
Exchange rate
The price of one currency in term of another currency.
Exchange rate index: the price of one currency in term of a basket of the other currencies, weighted according to the importance in the country’s international transaction.
Floating exchange rate
An exchange rate regime where the value of a currency is determined solely by the demand for and supply of the currency on the foreign exchange market.
The foreign exchange market
It does not exist in a simple location but is made up of banks and other financial intermediaries that buy and sell foreign currency on behalf of their private and business customers.
Depreciation
A decrease in the value of a country’s currency in a floating exchange rate system. (a decrease in the free market ER of a currency)
Appreciation
An increase in the value of a country’s currency in a floating exchange rate system. (an increase in the free market value of a currency)
需求哪一个国家的商品和服务,就会对哪一个国家的货币构成需求。 一个国家的商品和服务的export,会增加对该货币的需求 一个国家的商品和服务的import,会增加对该货币的供给
Factors that affect DS of one currency
- Import & Export
- Relative interest rate
- Relative inflation rate
- Investment from overseas in a country’s firms
- Speculation
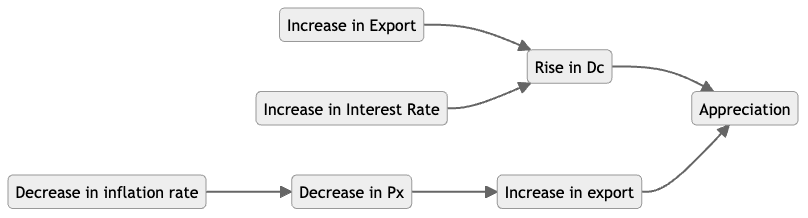
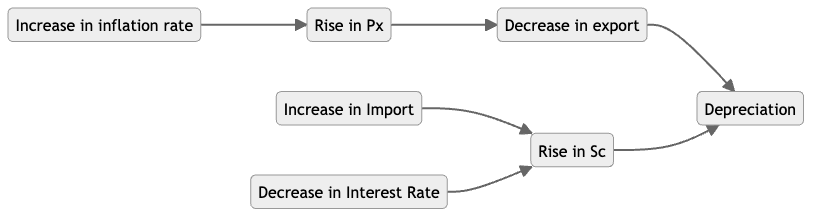
Floating ER system
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Freedom of domestic policies | Uncertainty for investors (A sudden exchange rate fluctuation might upset entrepreneurs' calculations and wipe out estimated profit) |
| Flexible response to external shocks | In floating exchange rate systems can cause rapid and major fluctuations which will further discourage trade and investment |
| Self-adjustment | Risk of imported inflation: floating ER system may worsen existing levels of inflation rate |
| No need to hold huge amount of foreign currency reserves | |
| Freedom of domestic policies |
Fixed ER system
One that is set as a particular level and maintained at that level by a government or central bank acting on behalf of the government.
Stability: more manageable handling of foreign debt
Advantages:
- Certainty for investors (simplify business plans/↓cost)
- Inflation control: fixed exchange rates ensure sensible government policies on inflation
- Protection against speculation: fixed exchange rates should reduce speculation in foreign EX
Disadvantages:
- Limitations on domestic policies (monetary policy -IR)
- Need to hold strong foreign currency reserves (protect against Speculation)
- Difficulties with setting rate
- International disagreements - low ER: vulnerability to charges of unfair competition)
Managed exchange rate
Where the currency is allowed to float, but with some interference from the government.
Overvalued currency
When the value of a currency is believed to be higher than what is perceived to be its market equilibrium value, based on its BoP position or its international purchasing power.
Undervalued currency
When the value of a currency is believed to be lower than what is perceived to be its market equilibrium value, based on its BoP position or its international purchasing power.
Advantages of Appreciation
- Cheaper imports→ Higher living standards
- Price of imports↓ → Expansion of plant & equipment (more Mof capital)
- Lower inflation rate (cheaper M → ↓inflationary pressure →may help economic growth)
- Competitive pressure on domestic producers forced to improve efficiency to remain competitive
Disadvantages of Appreciation
- More expensive exports →exports become less competitive while import become more attractive) → Contraction of export industries
- More cheaper imports → decrease in demand for home-produced products →Damage in domestic industries → Increased unemployment in export industries & in domestic industries which compete with imports
- Lower level of AD & real GDP (net exports ↓)
- Trade deficit may enlarge (X↓+ M↑)
No Comments