1. Measurement and uncertainties
Fundamental SI units
Fundamental units
| Quantity | SI unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | Kilogram | kg |
| Distance | Meter | m |
| Time | Second | s |
| Electric current | Ampere | A |
| Particle | Mole | mol |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Luminous intensity | Candela | cd |
Derived units
| Derived Unit | Measures | Derivation | Formal Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| hertz (Hz) | frequency | / s | s^-1^ |
| newton (N) | force | kg · (m/s^2^) | kg·m·s^-2^ |
| pascal (Pa) | pressure | N / m^2^ | kg·m^-1^·s^-2^ |
| joule (J) | energy or work | N · m | kg·m^2^·s^-2^ |
| watt (W) | power | J / s | kg·m^2^·s^-3^ |
| coulomb (C) | electric charge | A · s | A·s |
| volt (V) | electric potential | W / A | kg·m^2^·s^-3^·A^-1^ |
| farad (F) | electric capacitance | C / V | kg^-1^·m^-2^·s^4^·A^2^ |
| ohm (Ω) | electric resistance | V / A | kg·m^2^·s^-3^·A^-2^ |
| siemens (S) | electric conductance | A / V | kg^-1^·m^-2^·s^3^·A^2^ |
| weber (Wb) | magnetic flux | V · s | kg·m^2^·s^-2^·A^-1^ |
| tesla (T) | magnetic flux density | Wb / m^2^ | kg·s^-2^·A^-1^ |
| henry (H) | inductance | Wb / A | kg·m^2^·s^-2^·A^-2^ |
| degree Celsius (°C) | temperature | K - 273.15 | K |
| radian (rad) | plane angle | m·m^-1^ | |
| steradian (sr) | solid angle | m^2^·m^-2^ | |
| lumen (lm) | luminous flux | cd · sr | cd·sr |
| lux (lx) | illuminance | lm / m^2^ | cd·sr·m^-2^ |
| becquerel (Bq) | activity | / s | s^-1^ |
| gray (Gy) | absorbed dose | J / kg | m^2^·s^-2^ |
| sievert (Sv) | dose equivalent | Gy · (multiplier) | m^2^·s^-2^ |
| katal (kat) | catalytic activity | mol / s | mol·s^-1^ |
Scientific notation
Solar constant:
S = 1630 = 1.63 x 1000 = 1.63 x 10^3^ Wm^-2^
Three zero, ten to the third power
几个零,几次方
Permeability of free space:
μ~0~ = 0.0000004π = 4π x 0.0000001 = 4π x 10^-7^ TmA^-1^
Six zero and float begin at seven dights after point (小数点), ten to the seventh power
小数点后第几位,多少负次方
Metric multipliers
| Prefix | Abbreviation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| peta | P | 10^15^ |
| tera | T | 10^12^ |
| giga | G | 10^9^ |
| mega | M | 10^6^ |
| kilo | k | 10^3^ |
| hecto | h | 10^2^ |
| deca | da | 10^1^ |
| deci | d | 10^-1^ |
| centi | c | 10^-2^ |
| milli | m | 10^-3^ |
| micro | μ | 10^-6^ |
| nano | n | 10^-9^ |
| pico | p | 10^-12^ |
| femto | f | 10^-15^ |
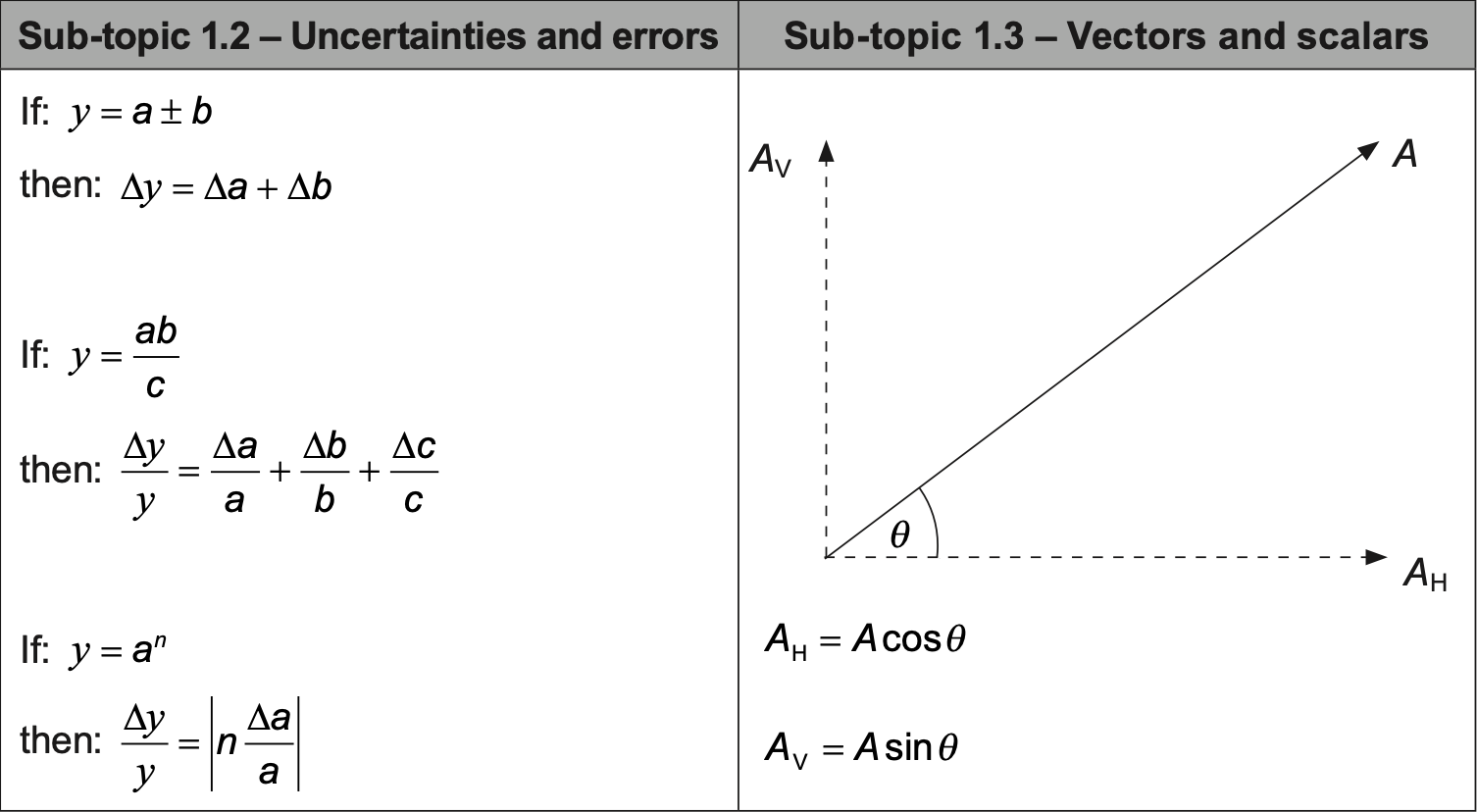
Random and systematic errors
| Random error | Systematic error |
|---|---|
| Caused by fluctuations in measurements centered around the true value (spread). | Caused by fixed shifts in measurements away from the true value. |
| Can be reduced by averaging over repeated measurements. | Cannot be reduced by averaging over repeated measurements. |
| Not caused by bias. | Caused by bias. |
- Accurate - Small Systematic error
- Precise - Small Random error {.grid-list}
Significant figures (digits)
All figures are significant except:
- Leading zeros
- Trailing (结尾) zeros, if this value does not have a decimal point
Calculation
Addition & Subtraction:
The answer must be equal to the least number of decimal places in the numbers added or subtracted
$$ \colorbox{#FF3B30}1\colorbox{#FFCC00}2.\colorbox{#007AFF}3\colorbox{#4CD964}6-\colorbox{#FF3B30}3.\colorbox{#FFCC00}1\colorbox{#007AFF}5\approx\colorbox{#FF3B30}9.\colorbox{#FFCC00}2\colorbox{#007AFF}1 $$
Multiplication & Division:
The answer must be equal to the least number of significant figure in the numbers multiplied or divided
$$ \colorbox{#FF3B30}3.\colorbox{#FFCC00}2\colorbox{#007AFF}1\times\colorbox{#FF3B30}4.\colorbox{#FFCC00}1\approx\colorbox{#FF3B30}1\colorbox{#FFCC00}3 $$
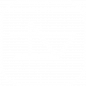
Uncertainties
| Addition & Subtraction | $y=a\pm b$ | $\Delta y=\Delta a+\Delta b$ (sum of absolute uncertainties) |
| Multiplication & Division | $y=a\times b$ | $\frac{\Delta y}{y}=\frac{\Delta a}{a}+\frac{\Delta b}{b}$ (sum of fractional uncertainties) |
| Power | $y=a^n$ | $\frac{\Delta y}{y}=\lvert n\rvert\times\frac{\Delta a}{a}$ (|n| times fractional uncertainty) |
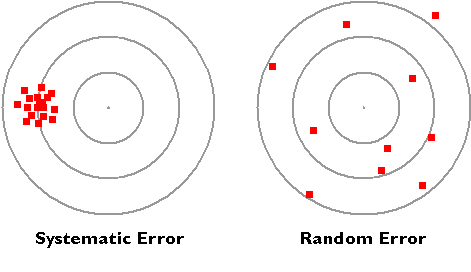
Vector
A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction
Scalar only has magnitude
No Comments