Monopoly
A monopoly
A market where one firm dominates the market for a good that has no substitutes and where significant barriers to entry exist.
- There is only one seller (price maker)
- The product is unique, there are no substitutes
- There are very high barriers to entry into and exit (high setting up cost) from the market
- Firms outside the market will lack perfect information
Barriers to entry
A range of obstacles that deter or prevent new firms from entering a market to compete with existing firms. (so, there is no difference between short-run and long-run)
- High fixed cost or setup cost
- Advertising and brand names with a high degree of consumer loyalty
- Economic of scale
- Patent
- The pace of product innovation
- Collaboration between existing producers to develop new products may act as a barrier
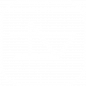
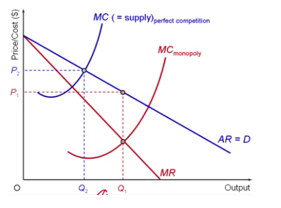
- Profit-maximising monopolist would choose the output where MC = MR.
- If the total revenue is higher than the production costs, it will make abnormal profit. This will be a permanent feature.
- In monopoly, there is no distinction between the short run and the long run because of the barriers that prevent the entry of competitors.
- There is no economic incentive for the monopolist to move away from the profit-maximizing output Q
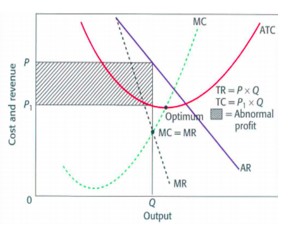
Natural monopoly
A firm that has economies of scale so large that it is possible for the single firm alone to supply the entire market at a lower average cost than two or more firms. It occurs in a market where the lowest costs can be achieved when only one firm sells to the market. It is typically associated with large fixed start-up costs.
If the market demand for a product is within the range of falling LRATC, this means that a single large firm can produce for the entire market at a lower average total cost than two or more smaller firms. When this occurs, the firm is called a natural monopoly.
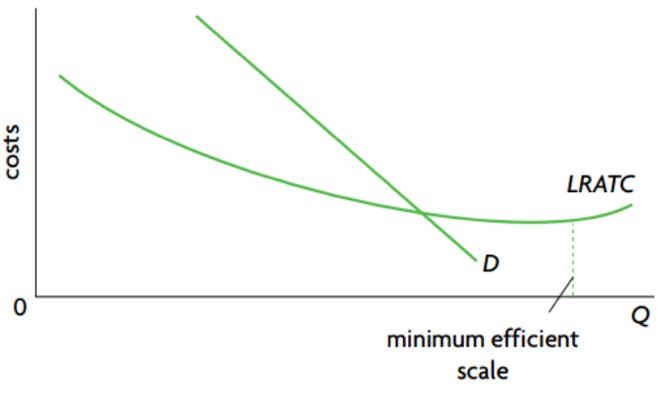
If new firm B enter the market, the market demand will be divided by firm A and B. Thus, the demand curve for firm A will be shifted leftward.
Outcomes of monopoly
- Higher price and lower output
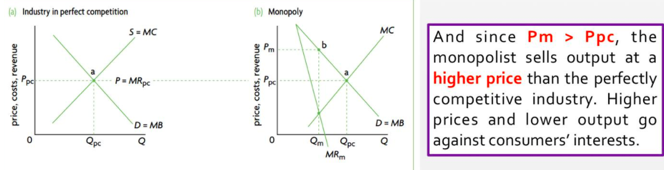
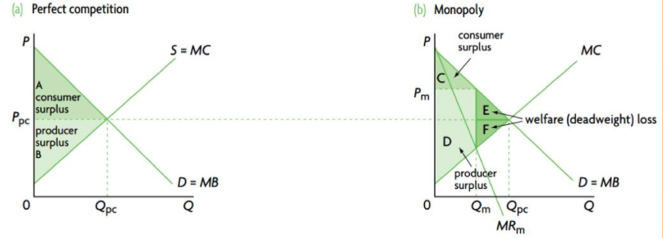
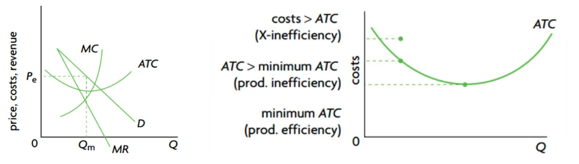
- Allocative inefficiency (MC is not equal to AR, loss of consumer and producer surplus)
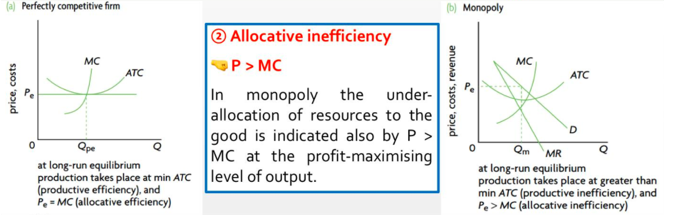
- Productive inefficiency (production at higher than minimum ATC)
a. Lack of competition in monopoly may lead to higher cost (X-inefficiency: producing at higher than necessary ATC) due to poor management, a poorly motivated workforce, lack of innovation and use of new technologies.
Policies:
-
Legislation (government can force the firm to charge a price equal to its average total cost)
-
Regulation
AD
- To promote competition by preventing collusion between oligopolistic firms.
- To manage and control mergers
- To ensure more socially desirable price and quantity outcomes
DIS
- The laws themselves may be vague, allowing much room for different interpretations
- Laws in particular country may be enforced to varying degrees.
- It is difficult to discover evidence of the collusion and to prove it
-
Nationalization (State ownership)
-
Trade liberalization (introduce foreign competitors)
-
Privatization (Encourage competition)
Situations which government should NOT control the monopoly power
- Natural monopolies (some are state-owned & do not aim to maximize profit)
- Ability to achieve economies of scale may lead to lower unit cost and price than a competitive industry
- Monopoly profits as a source of funds for investment / research & development
- They need to keep innovating to maintain economic profit
- Protect intellectual property right
- Protection of strategic industries against foreign competition
- Provision of otherwise profitable goods through price discrimination
Situations which government should control the monopoly power
- Abuse of monopoly power: higher price and lower output
- Less choice for consumers
- Abnormal profits are not justified
- Lack of competition: leads to lower incentive to improve & to innovate
- Allocative & productive inefficiency & misallocation of resources
Evaluation of monopoly compare to perfect competition market
Advantages:
- Ability to finance R&D
- Possibility of substantial Eos
Disadvantages:
- Higher price & lower output
- Lack of allocative & productive efficiency
- Lack of competition