Perfecr competition
Perfecr competition
Characteristics of perfect competition
- There are many buyers and sellers
- The product is homogeneous
- There is free entry into and exit from the market and buyers and sellers have perfect information
- No individual firm has any influence on the market price
- Each firm will seek to maximize its profit
- Perfectly competitive firms do not advertise as there is perfect knowledge and the products are homogeneous
Perfectly competition firms
Price takers
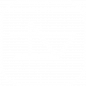
The price is set by the intersection of the market demand and supply curves. An individual firm’s output is too small to influence price and its average revenue equals marginal revenue.
In Short-run
Productive efficiency
Micro: is often measured in terms of long run average cost. A firm may be described as productively efficient if it is producing at the lowest point on the long run average cost curve.
- Achieved at AC = MC
Macro: Achieved when an economy is making full use of resources.
Allocative efficiency
Concerned with that resources are used to produce. It is achieved when resources are allocated to produce the right (merit) products in the right quantities (optimum).
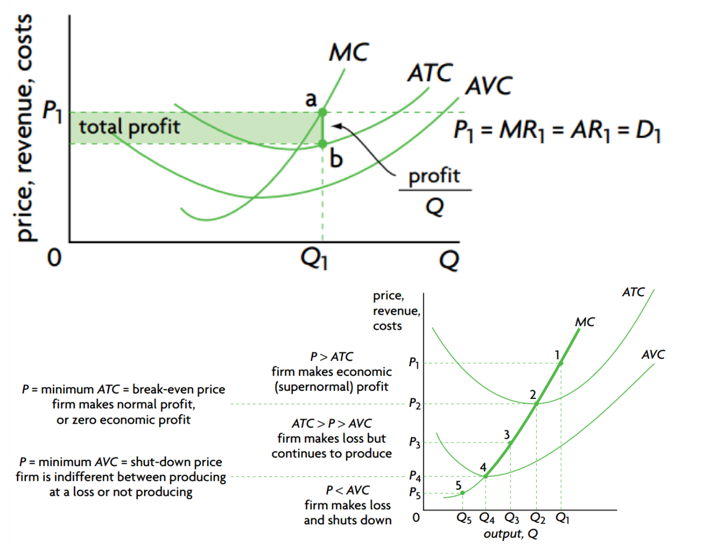
- It is achieved when MC=AR=P
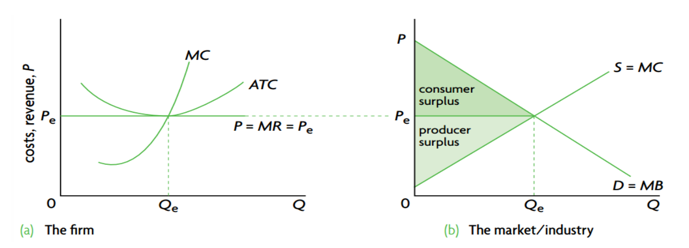
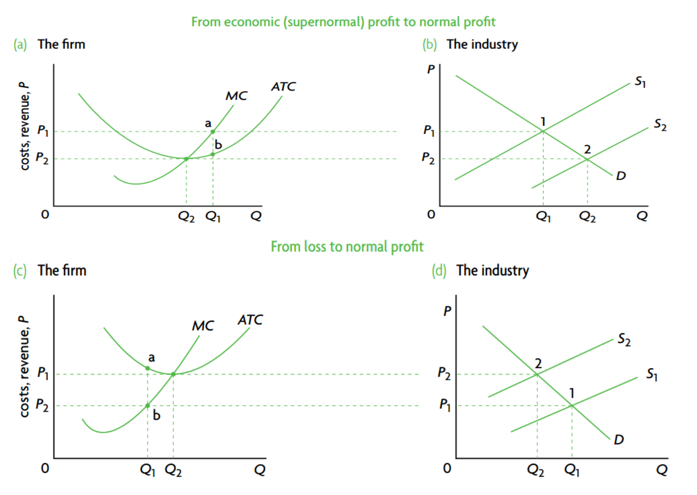
In long-run equilibrium under perfect competition, the firm achieves both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency. At the level of industry, social surplus is maximum, and MB=MC
Competition may promote efficiency by providing an incentive (in the form of profit) to the producers who make what consumers want at the lowest average cost and a punishment (in the form of going out of business) for those which do not keep the cost low and do not respond to changes in consumer demand.
Productive efficiency
- Low cost: high profit
- High cost: bankrupt
Allocative efficiency
- Produce goods in high demand: high profit
- Fail to produce what consumers demand: low profit
Evaluation of perfect competition market
Advantages:
- Allocative efficiency
- Productive efficiency
- Low prices for consumers
- Competition leads to the closing down of inefficient producers
- The market responds to consumer tastes
- The market responds to changes in technology or resources prices
Disadvantages:
- Unrealistic assumption
- Limited possibilities to take advantage of economies of scale
- Lack of product variety
- Waste of resources
- Limited ability to engage in research and development
- Market failure