Ultrastructure of cells
Prokaryotic cell structure
Prokaryotes have a simple cell structure without compartments
-
the cell does not have a nucleus
-
first organisms to evolve on Earth
-
simplest cell structure
-
small in size and found almost everywhere
-
some may have a cell wall that is thicker and stronger and can protect the cell, maintain its shape, and prevents it from bursting. contain peptidoglycan.
-
filled with cytoplasm
-
The 70S for ribosome in Svedberg units
-
contains DNA, usually 1 circular DNA molecule. Nucleoid is the place that contains DNA
-
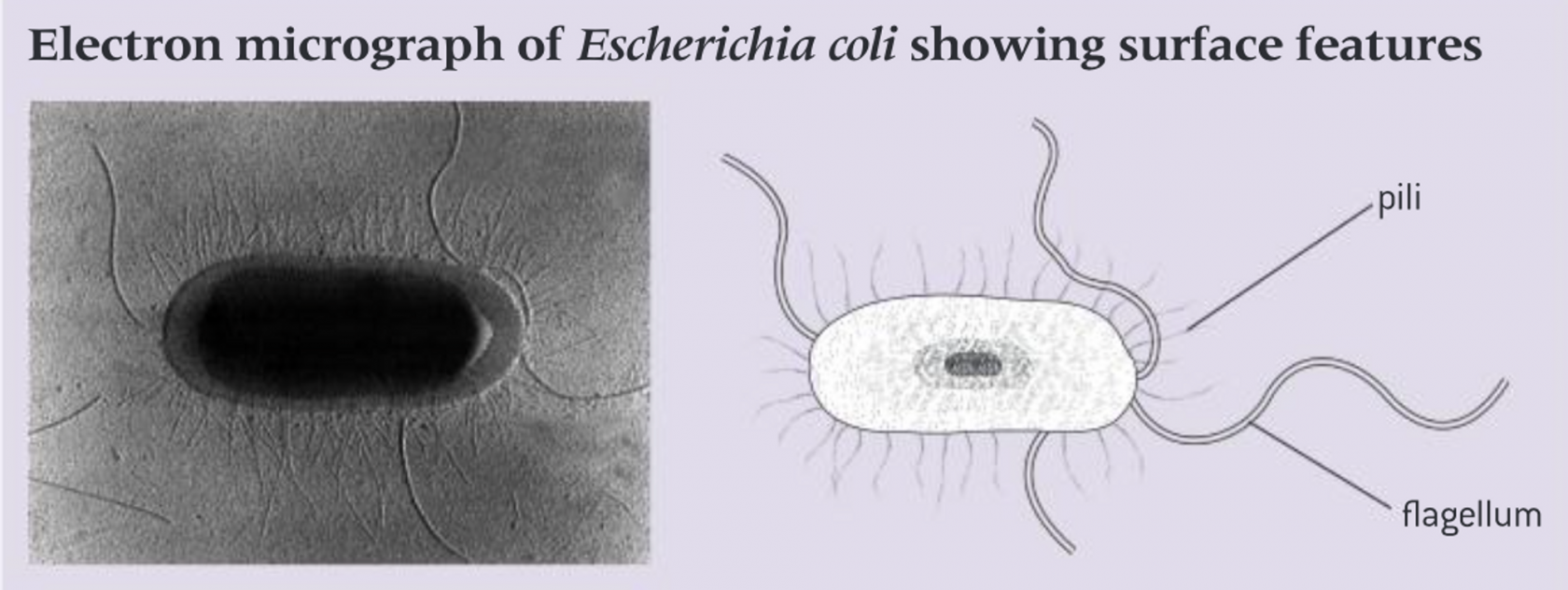
contains plasmids, a circular DNA found outside the nuclear zone, often carry genes for resistance to antibiotics and may be exchanged through pili to learn
-
Drawing prokaryotic cells
Cell division in prokaryotes
Prokaryotes divide by binary fission
-
used for asexual reproduction
-
binary fission
the single circular chromosome is replicated and the 2 copies of chromosomes move to opposite ends of cell. Division of cytoplasm quickly follows. Each of the daughter cells contains one copy of the chromosome so they are genetically identical.
Eukaryotic cell structure
Eukaryotes have a compartmentalized cell structure
-
advantages in being compartmentalized
- enzymes and substrates for particular process can be much more concentrated than if they were spread throughout the cytoplasm
- Substances that could cause damage to the cell can be kept inside the membrane of an organelle
- Condition such as pH can be maintained at an ideal level for a particular process, which may be different to the levels needed for other processes in a cell
- Organelles with their contents can be moved around within the cell
-
Nucleus

- double membrane and has pore
- contains chromosomes, consisting of DNA associated with histone proteins
- uncoiled chromosomes are called chromatin and often densely staining around the edge of nucleus
-
Golgi apparatus

- consists of cistenae
- have many vesicles nearby
- do not have attached ribosomes
- processes proteins brought in vesicles from rER, then carried in vesicles to plasma membrane for secretion
-
Lysosome

- single membrane
- contain high concentrations of protein and digestive enzymes
- break down ingested food in vesicles or break down organelles or even whole cell
-
Mitochondria

- double membrane
- produce ATP by aerobic cell respiration
- fat is digested here if it is being used as an energy source
-
Free ribosomes

- synthesis protein, releasing it to work in cytoplasm
- constructed in nucleolus
-
Chloroplast

- double membrane
- produce glucose and a wide variety of other organic compounds by photosynthesis
-
Vacuoles and vesicles

- organelles consist simply of a single membrane with fluid inside
- transport material inside cells
- digest foods inside vacuoles
-
Microtubules and centrioles

- moving chromosomes during mitosis
-
Cilia and flagella

- projecting from the cell surface
- usually only 1 flagella present
- can be used for locomotion运动
- cilia also can create a current in the fluid next to the cells
-
Rough endoplasmic reticulum

- consists of flattened membrane sacs, called cistenae
- attached to ribosomes (80S)
- proteins synthesize for secretion from the cell, carried by vesicles which bud off and are moved to the Golgi apparatus
-
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum